What is an Ontology?
By Saumye NavarathnaThe term ontology refers to a concept of knowledge representation which is still not vastly used. Simply, an ontology is a model of knowledge related to a certain domain into a set of concepts and relationships among them.
What is it used for?
Sematic web is the generation of web which the machines know what we are querying about. Simply, when we google something, google will return everything associated with the words entered to the search engine. But the search engine has not understood what we are looking for. Semantic web is where that the machine understands what we queried and return the results related. It is about the difference between data and knowledge.
In semantic web, it is needed to store data in a way that can be interpreted by the machines. To accomplish that the concept of ontological databases is introduced.
What is the difference?
The purpose of a normal database that we use is, to structure and store some data for querying. These data can not be understood by machines, even it is harder to understood by a developer other than the ones who developed the schema.
Ontologies also align with the normal databases about storing data and querying on them. And this type of databases carry the feature of meanings of data stored within.
What is in it?
An ontological database is comprised of classes and individuals. As we all can guess, class is a collection of individuals or objects. On the other hand, individuals are the knowledge stored in it, which is an instance of a class. It can be a concrete object or an abstract one.
How to create an ontological database?
There are few tools that can be used to develop ontological databases.
- DogmaModeler
- Protégé
- Onto-animal tools
- OWL Tools
Since ontological databases are used for advance concepts of computations, it is recommended to follow few steps before getting into developing an ontological database.
- Determine the domain and scope of the ontology.
- Consider reusing existing ontologies.
- Enumerate important terms.
- Define the classes & class hierarchy.
- Define the properties of classes.
- Define the facets of the slots.
- Create instances.
For this article, I will be using web protégé tool as the development tool.
Step 1
Go to Protégé web site and click Use webProtégé. It may require to signup for an account, continue for the main page by completing signup or signing.

You will be directed to a page where you can create and manage your ontological databases.
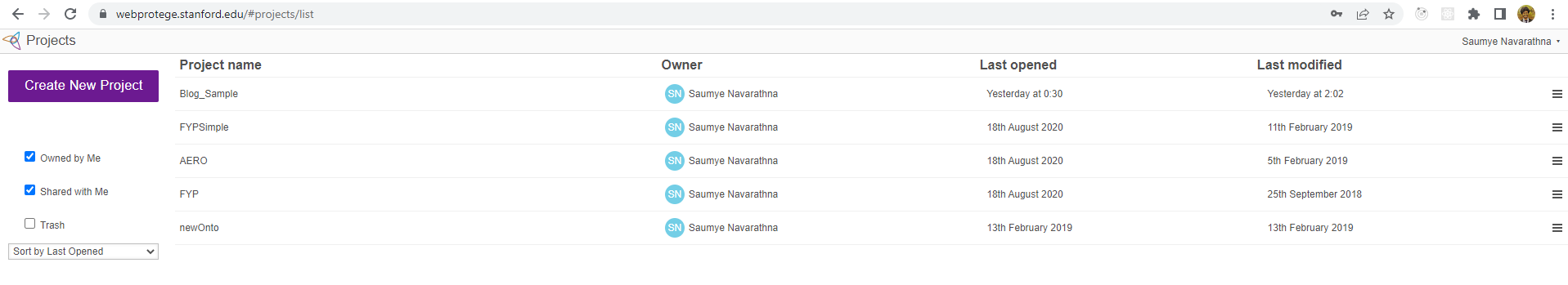
Step 2
By clicking new project, you can start a project and can continue developing the ontological database. You can add any name you like as the project name but recommended to have a meaningful name as the project name. You can specify the language that you are going to work with, or you can leave it empty. But when you specify a language and hope to go further with that, sometimes you may experience some limitations and errors while querying or using the database. But those problems will be addressed soon since these are still not fully developed platforms. Also, you can add a description about your work in the description area. There is an option for importing database as well. As same as in normal databases, the ontological database also can be exported and imported. After adding desired information, you can create the project. It will be added into the list of projects.
Step 3
You can select any of your projects and mange those from the main page. By clicking any of them, you will directed to a page where you can create, edit or delete artifacts of the database.
When you first get into any of your projects, you will see a class being created by default named Thing. This is taken as the class of everything, where we create our domain related classes as children to this Thing class. Anyone can get rid of the default concept of Thing class as well, but not recomended.
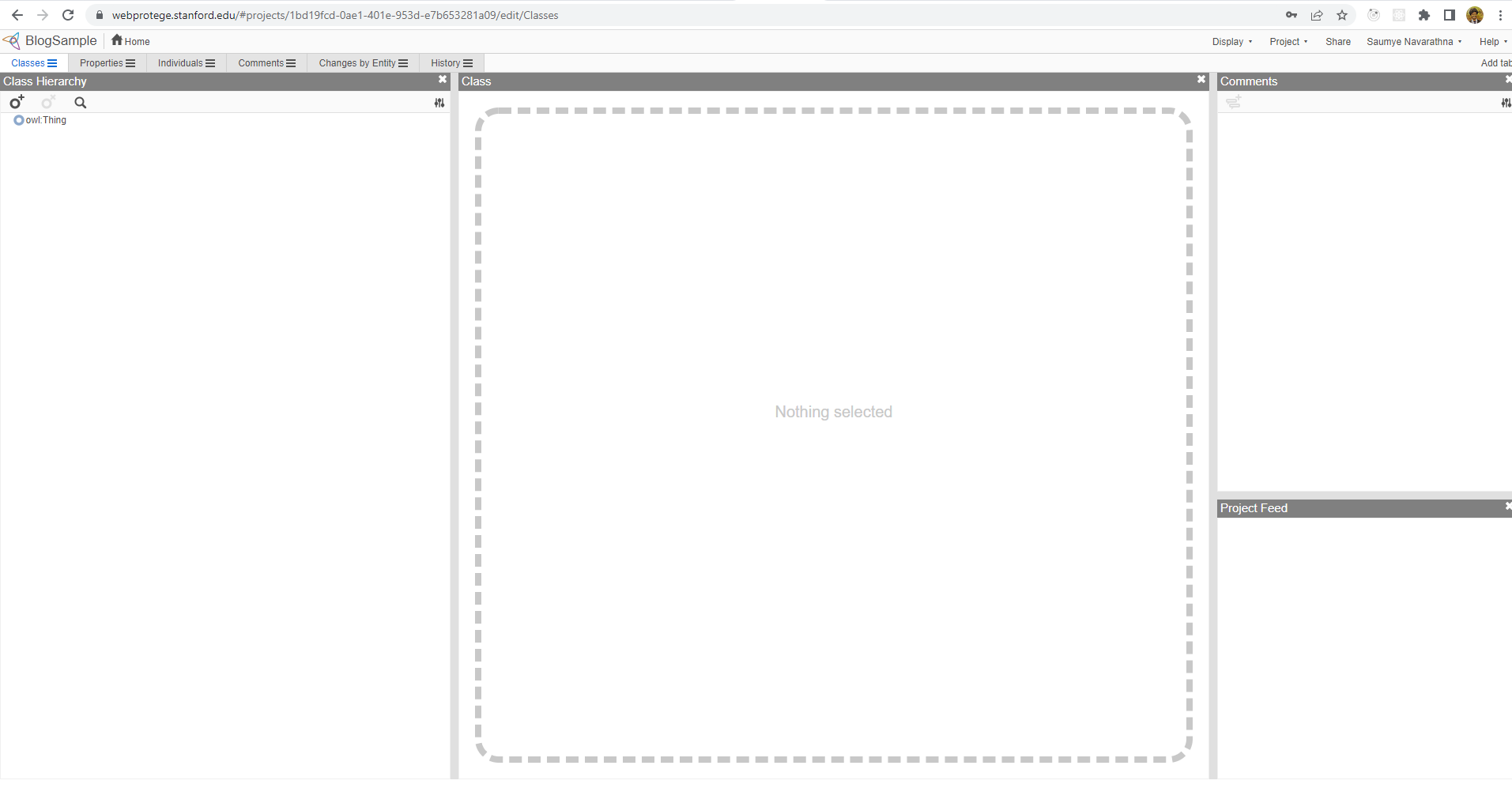
The window contains few tabs related to development of an ontological database.
- Classes In this tab we create classes where a class is a collection of objects and group of objects.
-
Properties In this tab we create properties which can be an object property or data property. Where object properties are the relation between classes and data properties are literals associated as same as the object properties. Ex: Object properties: {Man} eats {Rice} Eats is the object property {Man} name {Steve} Name is the data property
- Individuals These are the instances or the real world/ ground level components of an ontology. These can be imaginary as well.
Step 4
After creating all the classes, properties and individuals, we can export out database as an OWL file to be used in the projects as a database. To query data in OWL file, there are several types of libraries introduced. It can be used in projects of python, java, C# and etc. Also, there are frameworks that supports ontological databases. Here are some libraries that can be used for data manipulations and queries on an ontological database.
- Owlready2 - python
- Ontospy – python
- The OWL API – java
- Owldotnetapi - c# / .net
- Rowlex – c# / .net
Example
Let’s think of the most popular database example of the teachers and the students. We have teachers who teach the modules, and students who learn the modules.
Let’s create our classes first. We have the Thing class which is the parent class for all the things. If we think about the entities, they are Teacher, Student and Module. But Teacher and Student also will have some properties in common. That makes us to make two sub classes for which will comprise teachers and students into one and modules into the other. We will create sub classes for Module and Teacher and Student classes as sub classes for the Person class.
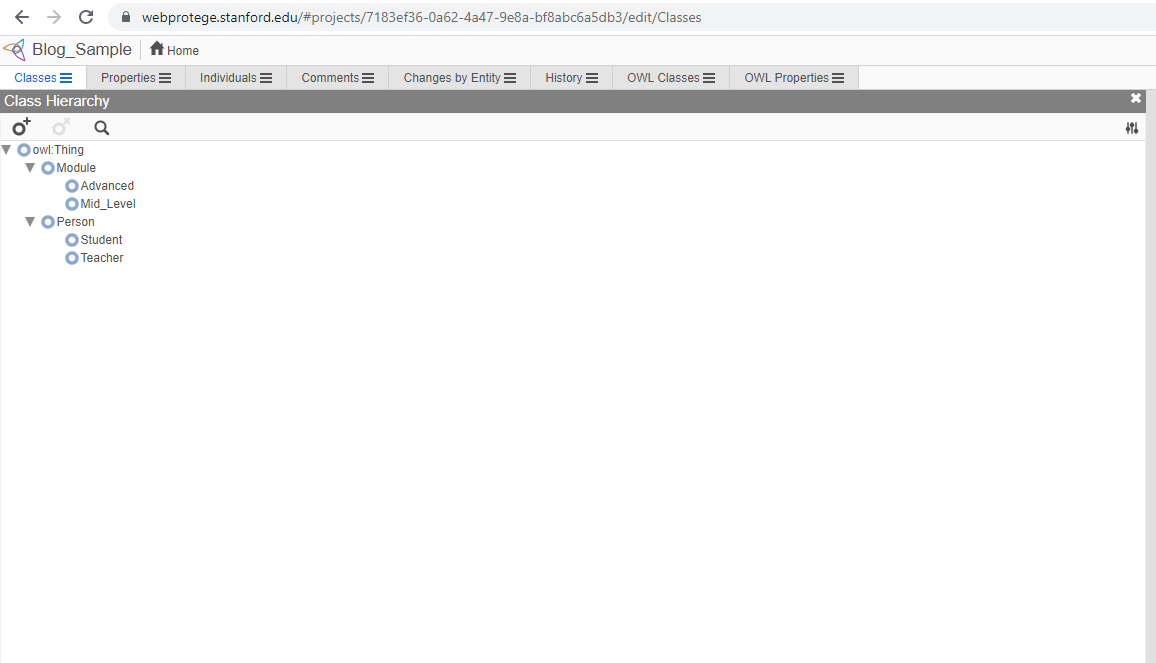
After creating out classes, now we can create object properties for those classes. By navigating to properties tab, you can simply create them. As same as in the classes, the default property topObjectProperty holds the parental position for all object properties. When we create object properties, we can assign domain and a range for the property. For an example, students study the modules, so if we create property as studies, the domain will be students and range will be modules. If we create a property as enrolledB,y the domain will be modules and range will be students.
Let’s create properties as studies and teaches.
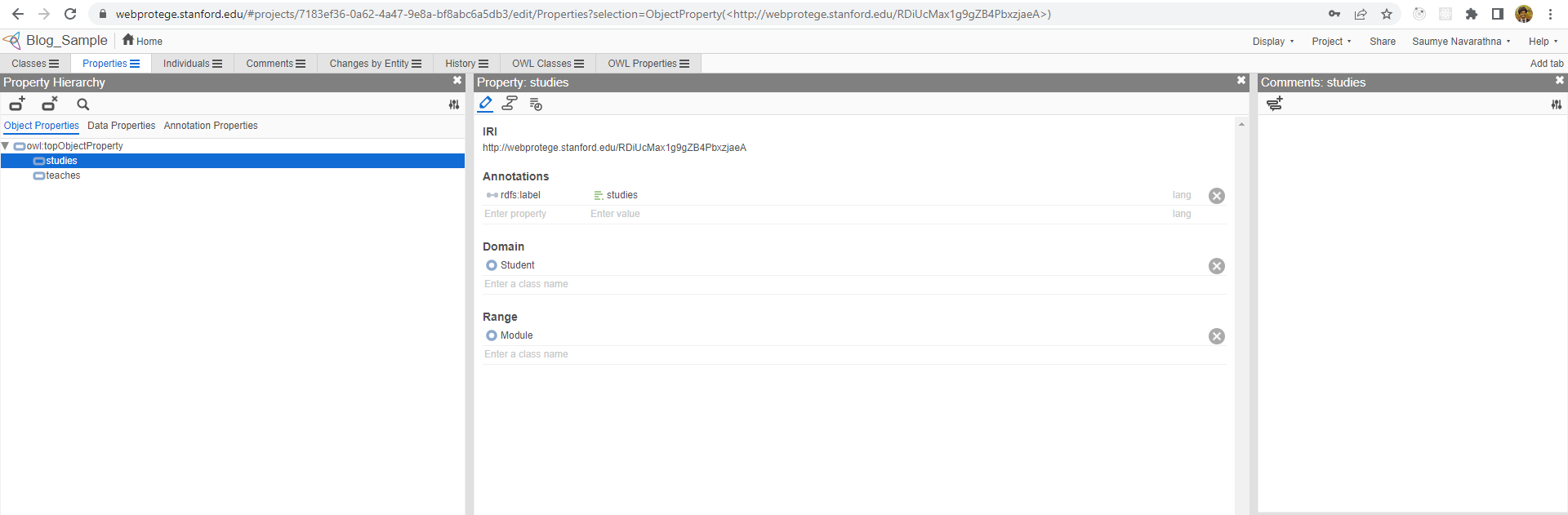
Let’s create some data properties for our domain. We can add those by navigating to data properties tab inside the properties tab. As same as classes and object properties, there is a parent property named as topDataProperty. We create all the data properties as sub properties to this. We can think of having some data properties as name, index_number, staff_number. Let’s create them. For these properties also we can have domain and range. But the range will always be a literal type, such as string, int, and etc.
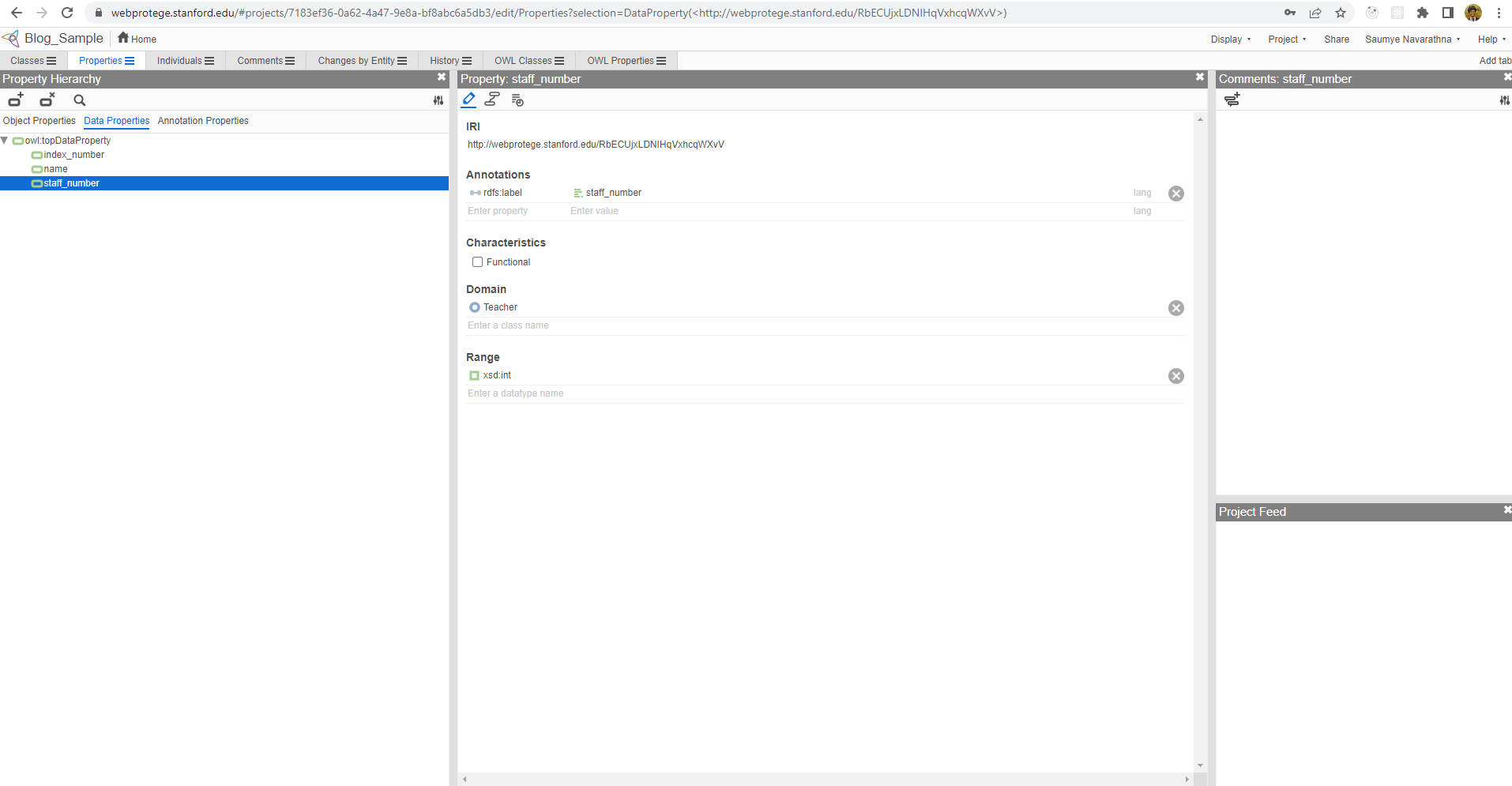
Our ontology is ready to have its data, which is called individuals in ontological database. First we can create modules such as Mathematics, Science, IT. To do this, select the class Module from hierarchical view and click create button and add the names in dialog box.
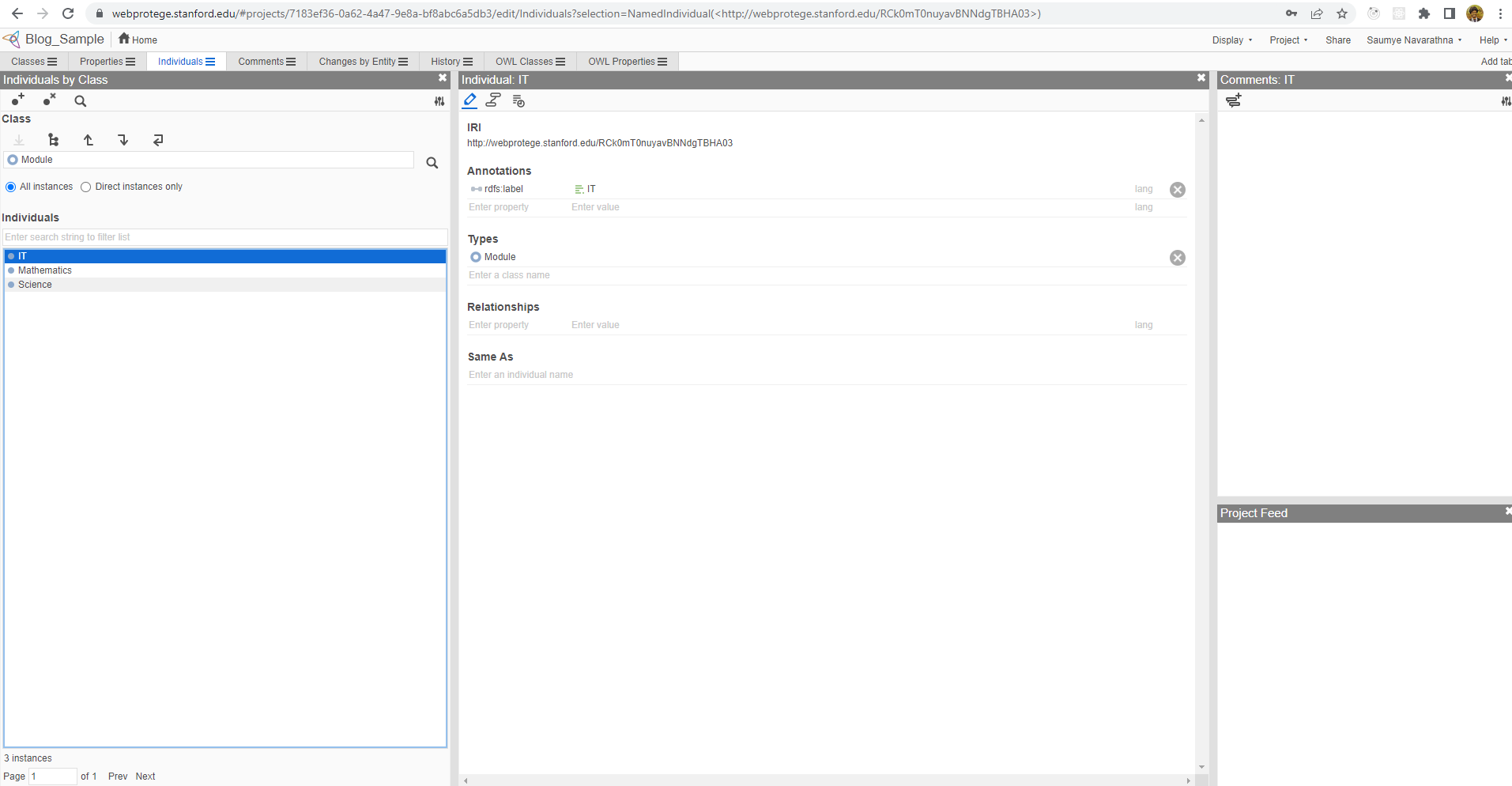
In the same manner, we can create some teachers and students. But when adding students, we can add the properties we created as well.
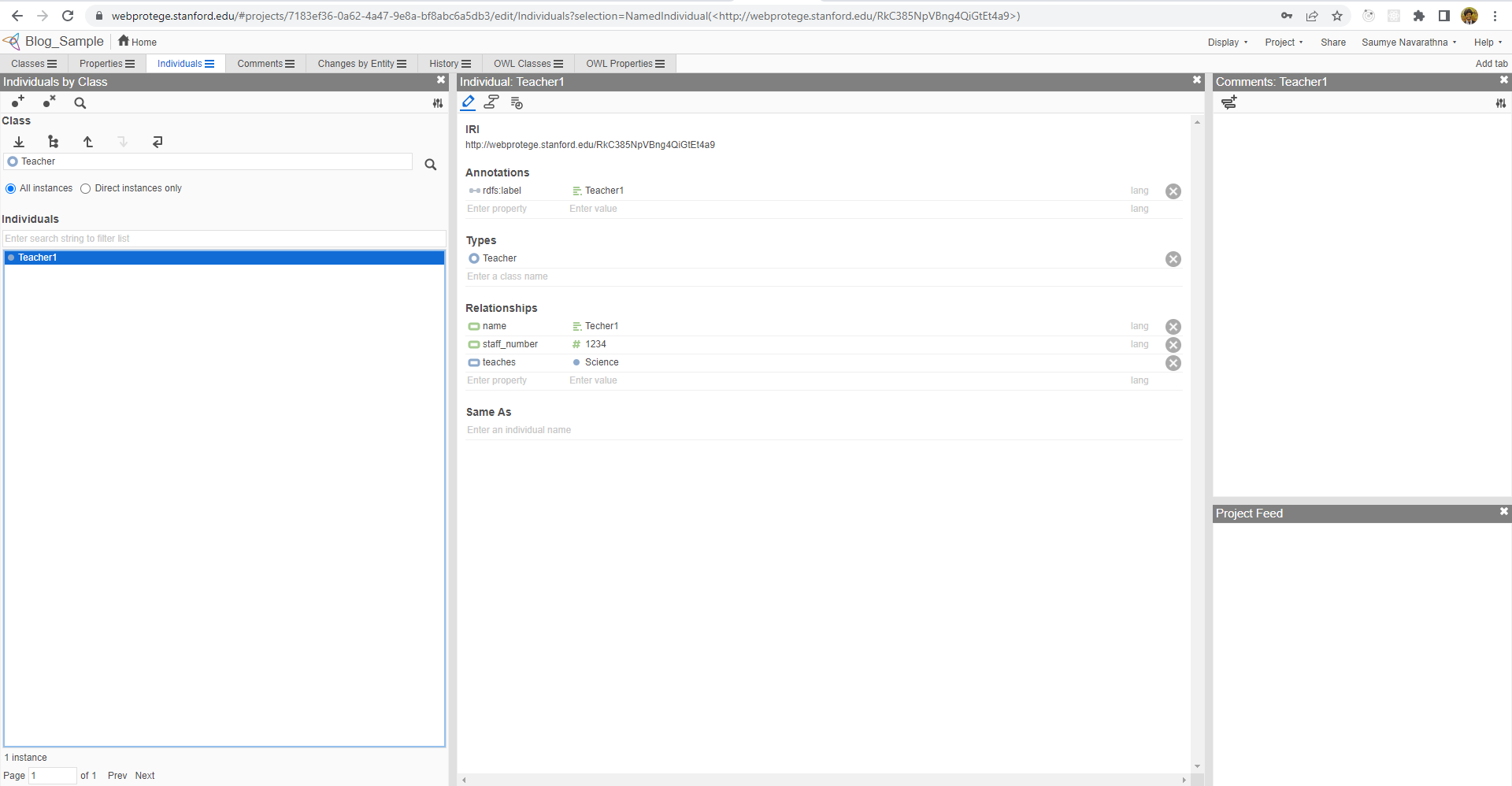
The final outcome of the knowledge representation will be like this for a teacher. It will be complex for more detailed and complex knowledge bases and hard to determine classes and relationships in the most effective manner.
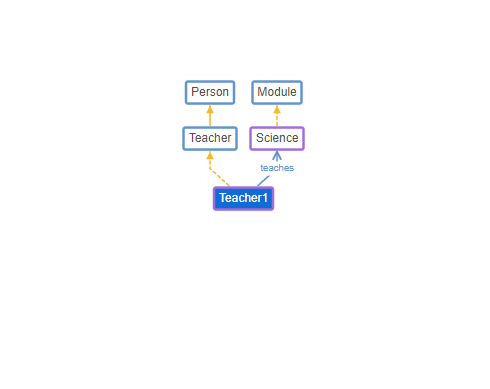
Now we are ready to export our database and use it in a real project. We will discuss about that in upcoming post.
References
- https://protege.stanford.edu/
- https://www.w3.org/
- https://journalofbigdata.springeropen.com/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article
- https://pypi.org/