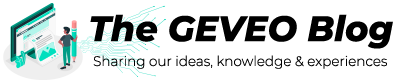New Features in .NET7.
By Sachintha GunathilakaMicrosoft’s .NET platform is a powerful and versatile tool for building a wide range of applications. With each new release, .NET continues to evolve and add new features and improvements that make it even better. The latest release, .NET 7, brings several new features and improvements that developers should be excited about.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the most important new features of .NET 7 and how they can help developers build better applications.
On-stack replacement (OSR)
On-stack replacement (OSR) is a new feature introduced in .NET 7 that allows the runtime to replace the executing code of a running method with a new version of the code, without stopping or restarting the method. This can help to improve the performance of long-running methods, by allowing the runtime to optimize the code as it runs.
On-stack replacement (OSR) allows the JIT compiler to generate native code for a method while it’s executing and replace the executing code with the new code at any point in the method’s execution. This means that the runtime can optimize the code based on the actual runtime behavior of the method, rather than just at specific points in the method.
The process of replacing the executing code with the new code is done by performing a context switch in the runtime. The context switch saves the current state of the executing method, including the stack and registers, and switches to the new version of the code. The new code is then executed with the saved state of the method.OSR is useful for optimizing long-running methods that may have different execution paths, or that may change behavior based on the input data. By generating and replacing code as the method runs, the runtime can optimize the code based on the actual behavior of the method, which can lead to significant performance improvements.
Regex Improvements
Regular expressions, or regex, are a powerful tool for searching and manipulating text. .NET 7 introduces several improvements to its regex engine, including new syntax and performance improvements.
One of the main improvements to the .NET regex engine is the addition of the “balanced groups” syntax. Balanced groups allow you to match nested constructs, even if the text contains other nested pairs of the same construct. For example, suppose you have a string with nested parentheses, and you want to match the contents of the innermost pair of parentheses:
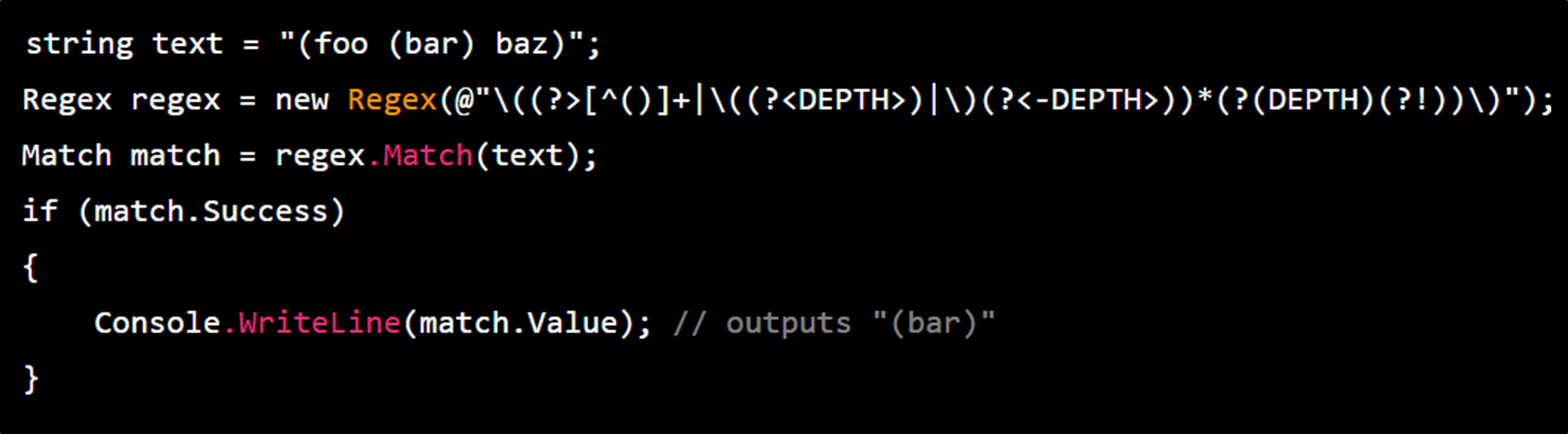
Another improvement to the .NET regex engine is the addition of the “skip” quantifier. The skip quantifier allows you to match a pattern but exclude it from the final match result. For example, suppose you have a string with a value between two delimiters, and you want to extract the value.
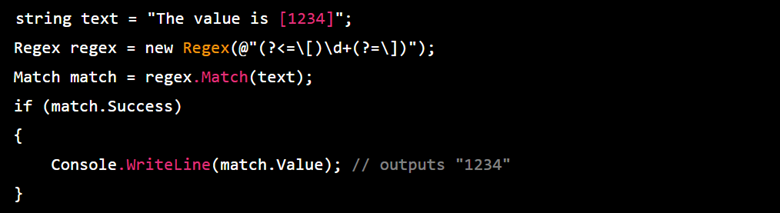
Another performance improvement is the use of “jit” or “just-in-time” compilation for regular expression patterns. It allows the regex engine to compile patterns into machine code at runtime, improving performance. For example, suppose you have a large string, and you want to find all occurrences of the word “hello”.
Simplified LINQ Ordering
LINQ, or Language-Integrated Query, is a powerful feature of .NET that allows you to query and manipulate data using a common syntax. One common use of LINQ is to sort data, either in ascending or descending order. DOT NET 7 introduces a simplified syntax for ordering data in LINQ queries.
In previous versions of .NET, sorting data in descending order required the use of the OrderByDescending method, followed by the ThenBy or ThenByDescending methods to specify additional sorting criteria.
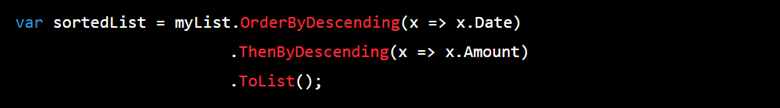
In .NET 7, you can now use the Order method to sort data in either ascending or descending order, with the direction specified by a new keyword: ascending or descending.
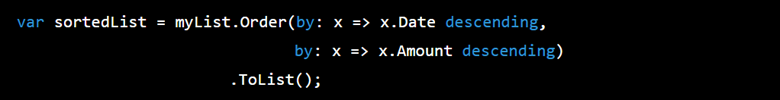
The new syntax makes it easier to read and write LINQ queries, especially for complex sorting scenarios where multiple sorting criteria are involved. Additionally, the Order method allows you to mix ascending and descending sorting directions within a single query, which was not possible with the previous syntax.
Application Trimming Improvements
Application trimming is a process of removing unused code and metadata from a .NET application to reduce its size and improve its performance. In .NET 7, there are several improvements to application trimming that make it more powerful and flexible:
-
Single-File Publish. .NET 6 introduced the ability to publish an application as a single-file executable, which packages the application and all its dependencies into a single file. In .NET 7, this feature has been improved to include application trimming, which removes unused code and metadata from the single-file executable.
-
Analyze Application Trimming Report. .NET 7 includes a new tool called dotnet-trim-analyzer that can be used to analyze the results of the application trimming process. The tool generates a report that shows which parts of the application were trimmed and why, helping you to identify any issues and optimize your application’s performance.
Reflection Improvements
Reflection is a powerful feature in .NET that allows you to inspect and manipulate types, objects, and assemblies at runtime. DOT NET 7 introduces several improvements to reflection, including AssemblyLoadContext for better memory usage and performance, metadata annotations to improve clarity and correctness, performance improvements by caching reflection data and reducing overhead, and new APIs for generating IL code at runtime. These improvements can help to make reflection more efficient, easier to use, and more powerful, opening up new possibilities for dynamic code generation and runtime introspection.
Dynamic PGO Improvements
Dynamic PGO (Profile-Guided Optimization) is a technique used to optimize compiled code based on runtime performance data. DOT NET 7 has introduced improvements to Dynamic PGO, including the ability to collect performance data across multiple runs of an application, use different optimization strategies for different parts of the code, and generate optimized code for more complex code patterns. These improvements can result in faster and more responsive applications, especially for large and complex codebases.
Conclusion
The new features and improvements in .NET 7 have significantly enhanced the framework, providing developers with a more efficient, powerful, and flexible development experience. The improvements include better performance through enhancements to the garbage collector and memory handling, and new APIs to support the development of web and cloud applications. Additionally, developers can enjoy a more streamlined and user-friendly experience with the simplification of LINQ ordering, as well as reflection and regex enhancements that make it easier to work with types and regular expressions. The addition of dynamic PGO improvements and application trimming further optimize the performance and size of .NET applications, while also improving startup times. Overall, these improvements make .NET 7 an even more robust and compelling framework for developers building and running .NET applications.
References
- https://www.bacancytechnology.com/blog/whats-new-in-net-7
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/core/whats-new/dotnet-7
- https://www.bytehide.com/blog/official-dotnet-7-features-released