Image Processing
By Malith KoswattegedaraWhat is Image Processing
Image processing is a field of knowledge that falls under computer vision. It is the manipulation of digital data to convert data into a suitable form for further analysis. The first recorded digital image was sent by a submarine cable from New York to London in the newspaper industry.

How it Works?
What is an Image -
An image is nothing more than a two-dimensional signal. It is defined by the mathematical function f(x,y) where x and y are the two co-ordinates horizontally and vertically. The value of f(x,y) at any point is gives the pixel value at that point of an image.
Types of Images
- Binary image – This image contains only two values for a pixel.

- 8-bit color format – Known as gray scale images. It has 256 different shades of colors.

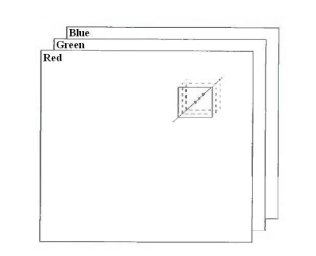
- 16-bit color format - Known as RGB images. A color image can be divided in to further three formats which are red, green and blue. Each format contains 8 bits per a pixel which means a color image contains 24 bits for a pixel.
Pixel Transforms
This is the simplest kind of operation that can be done to an image. Simply what happens here is based on a function input image pixel values will be changed.
Contrast Adjustment
In contrast adjustment, we can increase or decrease the image brightness. A function will be applied to every pixel in the image. For example, this function can be multiplying the pixel value by a constant and adding a constant value. the output image can be less or brighter.

Histogram Equalization
A histogram is a graph that shows the frequency of occurrence of data. In this graph, the x-axis represents pixel color value and the y-axis represents the number of occurrences of a particular color value.
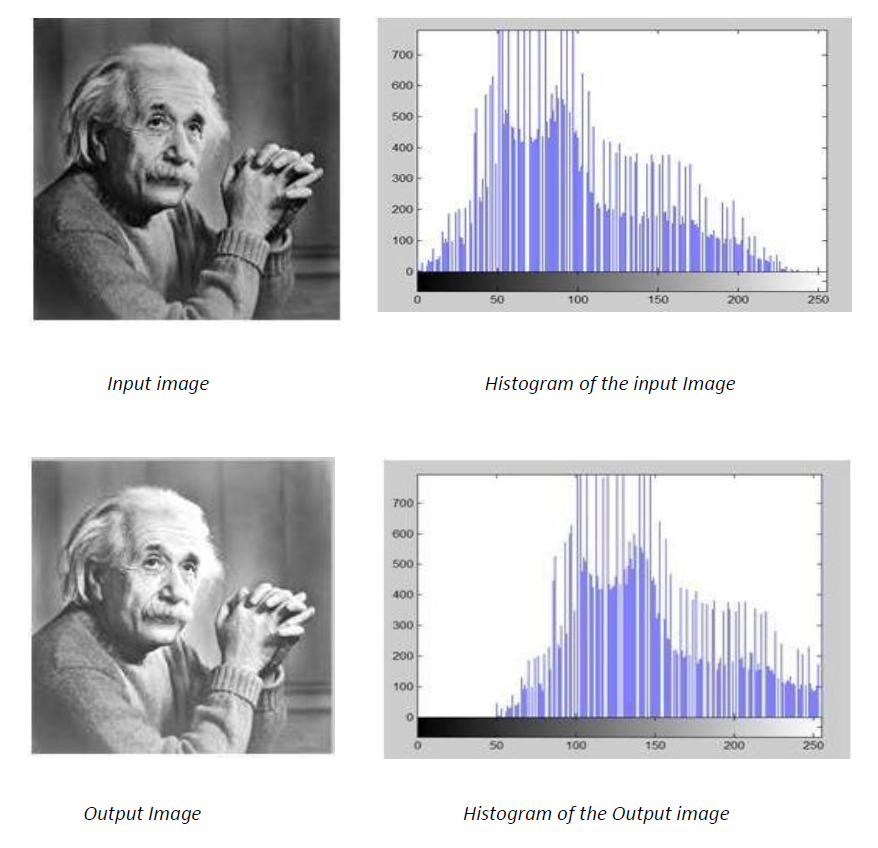
- Histogram sliding – In histogram sliding what happens is complete histogram graph will be shifted to left or right by changing the pixel values of an image. By doing this so many changes can be done in the image. For example, brightness change is shown in the below pictures.
- Histogram Stretching – Using this method contrast of the image can be increased. Contrast means the difference between the maximum and minimum pixel intensity. Using the following formula contrast of a gray image can be increased.
OpenCV
OpenCV is an open-source computer vision library. One of the main uses of OpenCV is image processing. Most of the image processing techniques can be simply done using this library including the operations discussed above.
Basic Image processing operations with OpenCV and python
Rotate Image Install the OpenCV.
pip install opencv-python
Import the library.
import cv2
Read the image.
img = cv2.imread("pyimg.jpg")
Display the image.
cv2.imshow('Original Image', img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
To get the width and height of the image.
height, width = img.shape[0:2]
Rotate image.
cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, scale)
In here center is the point of rotation, the angle is the degree of rotation, and the scale is the property which make the image fit on screen.
Crop image Get the height and width of the original image.
import cv2
img = cv2.imread("pyimg.jpg")
height, width = img.shape[0:2]
Now get the starting point and ending point of the new image. Image is a 2D array there for starting point and the ending point of the row and columns should be calculated.
startRow = int(height*.15)
startCol = int(width*.15)
endRow = int(height*.85)
endCol = int(width*.85)
Crop the image
croppedImage = img[startRow:endRow, startCol:endCol
Adjust image contrast In OpenCV there is no inbuild function to adjust the contrast. As discussed above following equation can be used to adjust the brightness.
new_img = a * original_img + b
If a is higher than one there will be higher contrast, if a is lower than one there will be lower contrast and if a is equal to one there will be no change. The values of b varies from -127 to 127. To implement the above equation addWeighted() method in OpenCv can be used.
cv2.addWeighted(source_img1, alpha1, source_img2, alpha2, beta)