Factors affecting Sprint planning efficiency
By Thusitha Kumara GabadageEvolvement of software projects happened gradually. Like all the other technologies, software development and project management modified over the time with the idea of reducing expenses and increasing quality. Software development faced more dynamic and rapid changes in competitive industry and this caused significant amount of difficulties such as changes of customer desires, timing restrictions, budget difficulties, communication issues, etc. came in to play. The word ‘Agile’ used to describe flexible rules of project behaviour, focuses on human interaction and iterative and incremental software development and the Agile software development methodologies began to emerge. Scrum is one Agile method that has been published as a formalized organisational pattern for software development.
Sprint Planning is the most important event, which is use to plan the work to be done in the next Sprint. The collaborative effort of the entire Scrum Team creates the Sprint plan and Scrum Master ensures that all the members understood the purpose. Planning is a complex task and critical for success of any software project. Sprint planning efficiency is to optimize resource usage and achieve minimal time or on time delivery. Company always tries to increase its profits and reduce costs. This is an essential challenge company need to achieve while fully utilizing its limited resources. When considering the software product business, this is mainly handle with planning and decision making for future releases and reduce cost while gaining more experience. Therefore, firm to be profitable and cost effective, needs to have efficiency in Sprint planning.
Objective behind the Sprint planning is to select the right set of requirements within the limitations and constraints and maximize the value for customers. Success or failure of the project will depend on how well team achieves this objective in each Sprint. During the planning need to find the right balance between customer requirements and resources available for development.
Efficient Sprint planning is compulsory in order to optimal resource utilization in reduced delay in delivery time. If the plan is accurate then there will be minimize work redundancy and reduce software defect density without putting extra burden on team members. Even though there is a standard Scrum specific planning in place, there are factors that can make planning inefficient. There can be technical factors and non-technical factors that can have negative influence over efficiency of Sprint planning. Inefficient sprint planning can cause many direct and indirect issues in the organisation.
Trust between customer and the team can degrade if team fails to deliver what they promised. Future of project will be difficult with unhappy customers and ultimately can lead to project failures. Since team gives the estimated Sprint plan, team is responsible to complete the plan work for the Sprint somehow. If sprint works under estimated team has to work over time to cover extra work. Then due to overtime work, quality of the product can be reduced, employees can be demotivated, due to the time limitation it can create aggressive team environment and can lead to conflicts among members. This can reduce team collaboration and leads to poor teamwork. If these issues occur, it will be a cost for the company. If organisation can reduce the inefficient sprint planning it will reduce these cost and add more benefits to the Agile software development process.
Creating a plan with the correct scope is vital otherwise resources will be wasted during the Sprint. Proper understanding, communication, selecting correct requirements, breakdown tasks, etc. need to be done efficiently during the planning in order to reduce resource wastage during the Sprint. Otherwise there will be delays and final outcome will be affected. Quality of the product will be a collection of iteration releases. If each iteration delivers quality output ultimate product will be a high quality product. Quality of the iteration output will be depending on the efficiency of the plan.
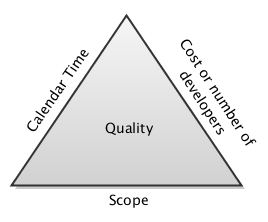
Triple constraint tradeoffs [Source: Internet]
To find the right balance among the triple constraints for the Sprint, efficient Sprint planning is required. Plan should adhere to time, cost and scope constraints and must be delivered on time within the cost while meeting the agreed scope. Changes in any constraint will result deviation unless Project Manager rebalances the effect of the change using other remaining constraints.
Following table lists few of significant factors that can affect the efficiency of planning and categorized under Technical and Sociocultural factors.
| Technical Factors | Sociocultural Factors |
|---|---|
| Requirement Volatility | Lack of team member involvement |
| Poor PBI estimates | Poor communication |
| Quality of the Requirement information | Lack of QA team involvement |
| Technical dependency | Team behaviour |
| Non-functional requirement ignorance | Product owner/Customer relationship |
| Clarity of ‘Definition of Done’ | Lack of domain knowledge |
| Defects and changes of previous implementation | Ineffective meeting time, Disturbing meeting place |
| Inefficient set of PBI selection | Inefficient Product Backlog preparation |
| Incomplete testing | Individual preparation |
| Quality level expectation | Team Leadership |
Factors affect for inefficient Sprint Planning
There are significant number of technical and non-technical factors that influence on the efficiency of Sprint planning. Not all of the above factors might affect in our context. Sprint plan is a small part of the entire project plan, by achieving sub goals efficiently will help to meet ultimate goal efficiently. Therefore, efficient Sprint planning is significant for the success of the project.
References
Schwaber, K, & Sutherland, J 2016, *The Scrum GuideTM: The Definitive Guide to *
Scrum: The Rules of the Game. Scrum.org and ScrumInc, 2014.
Klimeš, C, & Procházka, J 2006, New Approaches in Software Development. In Acta
Electrotechnica et Informatica,
Larman, C 2011, *Scaling lean agile large Scaling Lean & Agile: Large, Multisite or *
Offshore Delivery, Retrieved July 12, 2016
Cockburn, A 2007, *Agile Software Development: Software Development as a *
Cooperative Game. 2nd Edition. Pearson Education.
Gray, CF, Larson, EW 2006, Project Management: The Managerial Process, Special
Indian Edition, Tata McGraw-Hill Education.