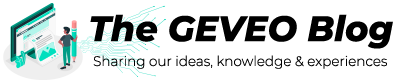Consensus Quorum.
By Priyadharsun Sivadasan.Enterprise Ethereum
Enterprise Ethereum refers to a defined set of guidelines and technical specifications to accelerate the adoption of blockchain technology among enterprises. The specifications provide businesses with the ability to leverage both Ethereum-based private chains and the public main net. The Enterprise Ethereum specification is maintained by the Enterprise Ethereum Alliance (EEA), a membership of blockchain and incumbent businesses from around the world. Quorum is ConsenSys’ Enterprise Ethereum solution. Using the Enterprise Ethereum guidelines and specifications determined by the EEA, ConsenSys Quorum is built to meet enterprise needs for blockchain-based solutions and applications.
Quorum
Quorum is a private blockchain platform that was created as a soft fork from Ethereum (ETH) in 2016 at JP Morgan Chase, one of the largest financial organizations in the world. Retaining much of Ethereum’s useful functionality, Quorum added enterprise-friendly features such as transaction privacy, permissioned access, and higher transaction throughput. Quorum is an open-source project any developer can contribute to. It is based on one of the original implementations of Ethereum. However, companies can create their own protected private networks on Quorum, a feature that is of critical importance to most enterprises. Being based on Ethereum, Quorum enjoys many of the advantages that come with Ethereum’s popularity and wide adoption. For example, the language used for smart contract development on Quorum is Solidity, the de facto programming language of choice on Ethereum. Since many blockchain developers are already familiar with Solidity, a company implementing Quorum will not have a lack of programming skills to access. Another advantage that comes from being based on Ethereum is tokenization. Similar to other private blockchains, Quorum lets businesses create their own tokens and coins. The tokens and coins based on Quorum are automatically compatible with Ethereum’s widely used token standards. The banking behemoth promoted Quorum as the ultimate blockchain solution for the finance industry. In 2020, JP Morgan Chase sold Quorum to ConsenSys, a technology and investment company specializing in Ethereum-based solutions. Reportedly, JP Morgan made a “strategic investment” in ConsenSys around the time of the deal.
ConsenSys Quorum
ConsenSys Quorum is an open-source protocol layer that enables enterprises to leverage Ethereum for their private or public production blockchain applications. Businesses can rely on ConsenSys Quorum to provide the enterprise-grade networks they need to unlock value with blockchain. On top of ConsenSys Quorum, you can integrate product modules from ConsenSys, third-party vendors, or your own in-house developers to build high-performance, customizable applications. Consensus Quorum has two different client Hyperledger Besu and Go-Quorum.
Hyperledger Besu vs Go-Quorum
Hyperledger Besu Stack Includes Hyperledger Besu, Orion and EthSigner. Hyperledger Besu is an open source Ethereum client maintained by the Hyperledger community, including ConsenSys. Besu is compatible with Mainnet, is based on Java, has obtained the Apache 2.0 license, and can be extended through its Java plug-in framework. As a production Ethereum client with mainnet function, Hyperledger Besu allows enterprises to use the value network and ecosystem of the Ethereum public chain and DApps on the chain with enterprise-level software. With the upgrade of Ethereum to Ethereum 2.0, Hyperledger Besu will have interoperability to ensure the seamless scalability and technical updates of the DApps built today. Orion is a private transaction manager for Hyperledger Besu client, developed under the Apache 2.0 license and written in Java. GoQuorum stack includes GoQuorum, Tessera and EthSigner. GoQuorum is an open source Ethereum client maintained by ConsenSys. GoQuorum is based on Go and is licensed under GPL. Tessera is a private transaction manager for the GoQuorum client, developed under the Apache 2.0 license and written in Java. EthSigner is a client-agnostic Ethereum transaction signer, written with Java and Apache 2.0 license. EthSigner provides private key storage and management by separating private key management from transaction verification.
Features of Consensys Quorum
- Permission Blockchain: Quorum blockchain is a permissioned blockchain, which means it does not give open access to all the participants. It is a blockchain consortium. A designated authority predetermines and approves the participants. This feature reduces the possibility of catastrophic breaches or failure.
- Performance: Quorum is faster than Bitcoin and Ethereum. It carries out more than 150 transactions per second. This is because of the simple consensus mechanism used by quorum. By default, quorum uses RAFT consensus for fault-tolerance and IBFT consensus for Byzantine fault tolerance, which is quite faster than Ethereum’s proof of work consensus
- Elimination of transaction pricing: It eliminated the concept of adding cost to a transaction using gas. There is no need for any cryptocurrency costs associated with running transactions on the quorum network. The Quorum code was initially forked off Ethereum, the usage of the gas itself exists but is set to zero.
- Better Privacy: Quorum provides on-chain public and private transactions. The open transactions are similar to Ethereum, whereas private transactions are not exposed to the public. It uses Constellation technology which encrypts specific messages in a place called an enclave and stores information about previous transactions.
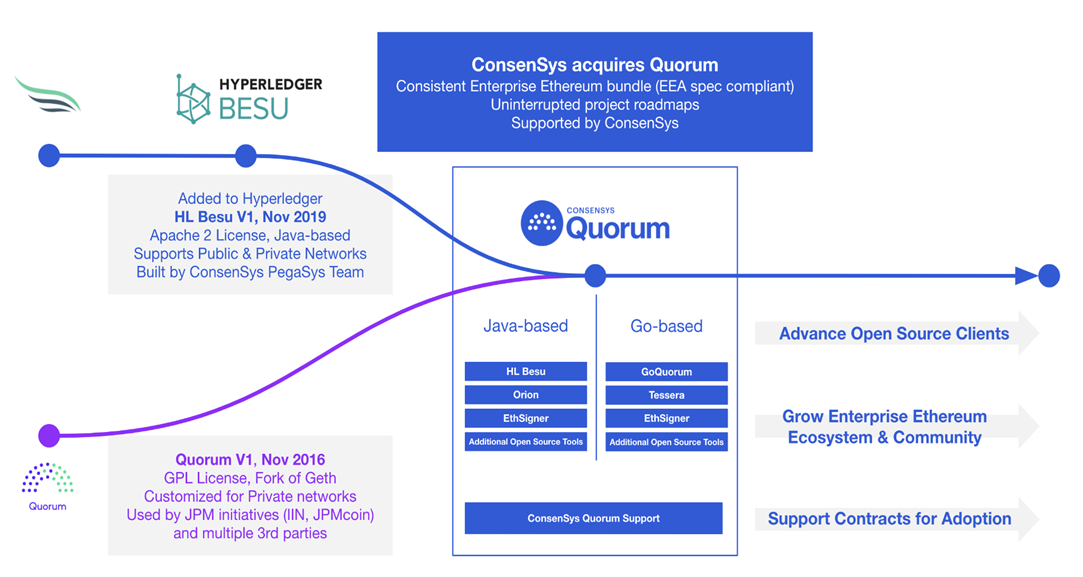
Quorum High level Architecture
- Quorum Node: It is a command-line tool that is a lightweight fork of Geth. It is configured only to allow connection from permission nodes, ditching the P2P connectivity.
- Constellation: It kept the transaction manager and enclave. It ensures that information added to the blockchain remains secure in every possible way.
- Transaction Manager: It takes care of the transaction privacy and ensures that the transaction data is encrypted during the process by storing the allowed access and other important data to facilitate the transactions.
- Enclave: It provides different cryptographic techniques such as participant authentication, transaction history, and other key functions to ensure that all the operations are performed optimally with a focus on scalability.
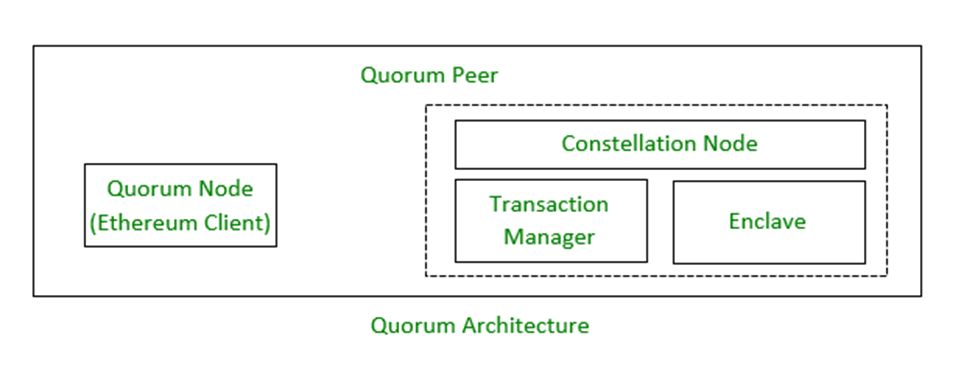
In this scenario, Party A and Party B are the part of the transaction AB while C is not included in this tx.
- Part A sends a Transaction Quorum Node A with the payload and setting privateFor to be the public keys for parties A and B.
- Quorum Node A pass that transaction to the Transaction Manager, requesting that it encrypt and store the transaction payload before forwarding it to the recipients of the transaction.
- Transaction manager of A will request Enclave to encrypt the payload for the given recipients.
- Enclave of party A encrypts the private tx payload by:
- Generating a symmetric key(tx-key) and two random nonces.
- Encrypting the tx payload with the tx-key and one of the nonce.
- Encrypt the tx-key separately for each recipient by:
- Sender’s Private key and Receiver Public key and get shared-key.
- Encrypt the shared-key with tx-key and the other nonce.
- Repeat for all the recipients.
- Return this to transaction manager
- Transaction manager store the response from the enclave and forwards to the private transaction recipients
- After that, the transaction manager of the party A send the encrypted payload to the GoQuorum Node and it will replace the data field of the transaction with that hash.
- Then tx is propagated to the network.
- The block containing tx AB is distributed to each GoQuorum node.
- Each GoQuorum will process that transaction and the transaction manager determine whether this node included in that transaction.
- Tx Manager of A&B are part of the transaction so they make a call to the enclave to decrypt the payload
- Party A&B’s enclaves decrypt the private tx.
- The transaction manager’s return their result to their GoQuorum Nodes.