Uncovering HashiCorp Vault Secrets
By Himasha Nahallage.The management of secrets and sensitive data has become a significant concern in the fast-paced IT world. A reliable and safe secret management solution is more important than ever as businesses adopt microservices and cloud-native architectures. We will look at HashiCorp Vault in this blog article, as it is an effective tool made to handle the challenges of managing secrets within modern IT settings.
Understanding the Need for Secret Management
The expansion of applications and services in the age of digital transformation increases the number of secrets-Passwords, PKI Certificates, SSH Keys, Key Value, API Keys, Encryption Keys (Symmetric and Asymmetric), Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP) and TLS Certs-that must be securely maintained. Traditional methods of managing secrets, such as storing credentials in configuration files or environment variables, are no longer adequate. The constant risk of data leaks and security breaches highlights the need for a centralized, secure solution.
Introducing HashiCorp and HashiCorp Vault

HashiCorp plays major role in the IT infrastructure sector and has its headquarters in San Francisco, California. As per the information available on various sources, in-order to help developers, operators, and security experts effectively manage cloud computing infrastructure, Mitchell Hashimoto and Armon Dadgar founded HashiCorp in 2012.
Their product line includes the following items, which they use to support various stages of the DevOps process:
- Terraform : This simplifies provisioning by allowing cloud infrastructure to be created by code.
- Packer : Increases productivity by making it easier to create reusable images for deployment.
- Nomad : This tool makes application management easier by providing container orchestration features.
- Vault : Offers strong secret management features that guarantee the protection of sensitive data.
- Vagrant : Makes testing and debugging easier by aiding in the creation of micro development environments.
- Consul : Facilitates communication by serving as a service mesh for container orchestrations.
- Waypoint : Enhances the software delivery pipeline by streamlining the development, deployment, and release of applications.
- Boundary : Controls user access to systems, improving access control and security.
Overall, HashiCorp's collection of solutions enables enterprises to optimize workflows, improve security, and accelerate cloud-based application deployments.

HashiCorp Vault is a solution designed to handle secrets and protect sensitive data in a variety of settings. Vault restricts access to secrets and encryption keys by authenticating against trusted sources of identification. This includes well-known authentication techniques including Active Directory, LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), Kubernetes, CloudFoundry, and numerous cloud platforms. Vault ensures that only authorized users and applications have access to sensitive information, improving organizational security and compliance.
Key Features of HashiCorp Vault
-
Secrets Management
The Vault is highly proficient in the secure storage and retrieval of sensitive information. A centralized vault is provided for the storage of secrets, with strict control over who can access them. There are two types of storages named as Integrated Storage (local or Consul) and External Storage (AWS, Azure, GCP).
-
Dynamic Secrets
The ability to produce dynamic, on-demand credentials (for AWS which is one of Vault’s best features) and TOTP (Revoke after). This strategy improves security by limiting the duration of credentials and lowering the risk associated with long-lived secrets.
-
Encrytion as a Service
Vault has strong encryption capabilities for both data at rest and data in transit. Vault offers a complete data protection solution, whether encrypting sensitive information or managing cryptographic keys.
- Data at Rest: When data is stored or saved, Vault ensures that it is encrypted, adding an extra layer of protection. This prevents unauthorized access to the stored data, even if someone gains physical access to the storage medium.
- Data in Transit: When data is being transmitted or moved from one point to another, Vault ensures that it is encrypted during the transfer. This safeguards the information from potential interception or eavesdropping by unauthorized parties.
-
Leasing and Renewal
Based on the lease, each secret may be valid for certain period (3 months, 6 months, etc.)
-
Revocation
Revoke secrets based on the user, bulk, type etc.
Use Cases
-
Authentication and Authorization
Vaults play an important role in securely managing resources. Through the inclusion of many authentication techniques, such as tokens and LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), Vault guarantees that sensitive data is only accessible by authorized entities.
1. Authentication Methods:
Vault offers a variety of authentication methods, which is critical for meeting differing security needs and infrastructures. Tokens and LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) can be given as examples, although Vault additionally offers a variety of authentication solutions.
- Token : These are cryptographic identifiers that used to authenticate users or entities. They offer a safe way to confirm identity and are frequently used in conjunction with other authentication methods.
- LDAP : A protocol called LDAP is used to maintain and provide access to distributed directory information services. By integrating with LDAP, Vault can use existing directory services for authentication purposes.
2. Ensuring Authorized Access:
By allowing different authentication methods, Vault ensures that only authorized entities, such as users, apps, or services, have access to sensitive information stored in the vault.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) : Administrators can build roles and assign rights based on job functions by using the RBAC concepts that Vault frequently applies. This ensures that people or systems can only access the resources required to complete their tasks.
- Fine-Grained Access Control : Administrators can use Vault to build fine-grained access controls, determining who can access certain secrets and conduct specific operations. This level of granularity improves security by reducing the likelihood of unwanted access.
3. Dynamic Secrets:
The ability of Vault to produce dynamic, short-lived credentials adds an extra degree of security. Vault can create unique credentials dynamically for every request, eliminating the risk of extended exposure to sensitive data by doing away with the need for static, long-lasting credentials.
-
Data Protection
Vault has the ability to encrypt data both in transit and at rest. This is especially helpful in situations where data privacy and compliance are top priorities.
-
Secure Key Management
Vault simplifies cryptographic key management by offering a safe and centralized store for handling encryption and decryption processes.
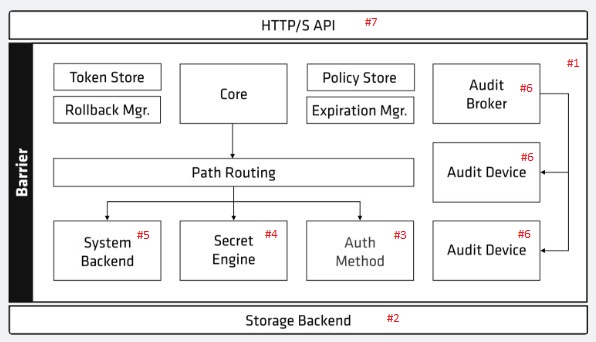
Vault Architecture
-
Vault's core engine contains storage, which acts as a vital layer for keeping sensitive data like passwords. The storage is loosely coupled, which allows for flexibility in implementation. However, the issue arises: where does this storage exist within Vault?
-
Raft storage is one option for storage within Vault; it is an in-built storage solution given by Vault. Raft storage is included by default with any Vault installation. Consul, another product from HashiCorp, can also be used to manage data storage. These two choices are known as HashiCorp-supported internal storage solutions. Vault also supports integration with other databases such as Oracle and MySQL, as well as cloud databases such as DynamoDB, Aurora, and Google Spanner, a multi-regional database. These external databases provide Vault with greater flexibility and scalability when it comes to storage management.
-
Auth is the entryway or entrance to Vault, and it determines how people connect to it. Users can login to Vault via a variety of identity providers, including Azure, GCP, AWS, Alibaba Cloud, and GitHub Authentication etc. By establishing trust, these identity providers make Vault secure.
-
The main function of Vault is to manage secrets, which it does by using a secret engine. The secret engine is loosely coupled, allowing you to manage a variety of secrets such as key-value pairs, database passwords, encryption keys for transit data, SSH keys, and more.
-
Vault's System Backend is responsible for keeping internal policies. These policies describe Vault's access control and authorization rules, determining which individuals or entities have permission to access certain secrets or execute specific operations.
-
Vault also includes auditing tools, which allow users to trace and monitor access to secrets. This audit functionality is useful for both compliance and security purposes. For example, if you want to know who accessed your AWS credentials three months ago, Vault can give detailed audit logs of access occurrences. These audit logs can be exported to multiple platforms, including Splunk, Syslog, Elasticsearch, and other audit plugins, for additional analysis and compliance reporting.
-
The HTTPS REST API can be used to securely access the vault. This provides a straightforward way to connect with Vault's functions programmatically, allowing users to automate operations and link Vault with other systems and tools in their network.
Other Integrations
HashiCorp Vault works smoothly with other DevOps tools and services. Let's look at its interactions with Datadog and OpenShift.
- Datadog Integration
The integration of HashiCorp Vault and Datadog enables extensive monitoring and observability of Vault's operations and security posture. Users can use this connection to obtain insight into Vault's performance metrics, such as request rates, latency, and error rates, as well as monitor security-related events like secret access and authentication attempts. The dashboards and alarms offered by Datadog assist guarantee the availability and adherence to security protocols of Vault while offering insight into its overall health. Users can also use Datadog's logging and tracing features to correlate Vault activities with other components of their infrastructure, which helps with troubleshooting and performance optimization.
- OpenShift Integration
Vault works smoothly with OpenShift, allowing enterprises to use Vault's features in containerized deployments. Vault delivers a secure foundation for OpenShift applications by managing microservice secrets and providing encryption for containerized data.
Security Best Practices
The HashiCorp Vault must also be secured, just like any other powerful tool. By putting security best practices into effect, such as multi-factor authentication, frequent audits, and appropriate disaster recovery planning, we can make sure that Vault alone stays a reliable and secure component of our infrastructure.
Conclusion
HashiCorp Vault stands out in the secret management arena due to its extensive feature set and adaptability. It's a crucial tool for companies looking to strengthen their security posture in a quickly changing IT environment, thanks to its features, use cases, and integrations. For more information, see the sources and official documentation listed below, as well as the community.
References
- HashiCorp Website: https://www.hashicorp.com/
- HashiCorp Vault Official Website: https://www.vaultproject.io/
- HashiCorp Vault Official Documentation: https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs
- Datadog: https://docs.datadoghq.com/all_guides/
- OpenShift: https://docs.openshift.com/