The Future of Big Data with Quantum Computing
By Asangika SandaminiWe live in the age of technology, but there’s still plenty to come. In recent years, large companies have been taking small, but important steps forward in quantum computing, which looks set to revolutionize the world as we know it. Quantum computers could spur the development of new breakthroughs in science, medications to save lives, machine learning methods to diagnose illnesses sooner, materials to make more efficient devices and structures.
What is Quantum Computing?
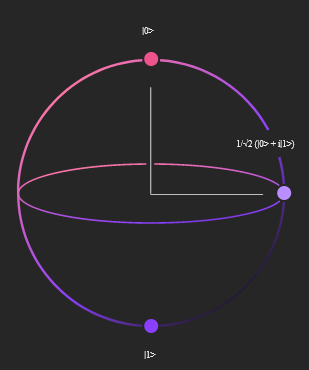
Quantum computers process information in a fundamentally different way than classical computers. Traditional computers operate on binary bits, information processed in the form of ones or zeroes. But quantum computers transmit information via quantum bits, or qubits, which can exist either as one or zero or both simultaneously.
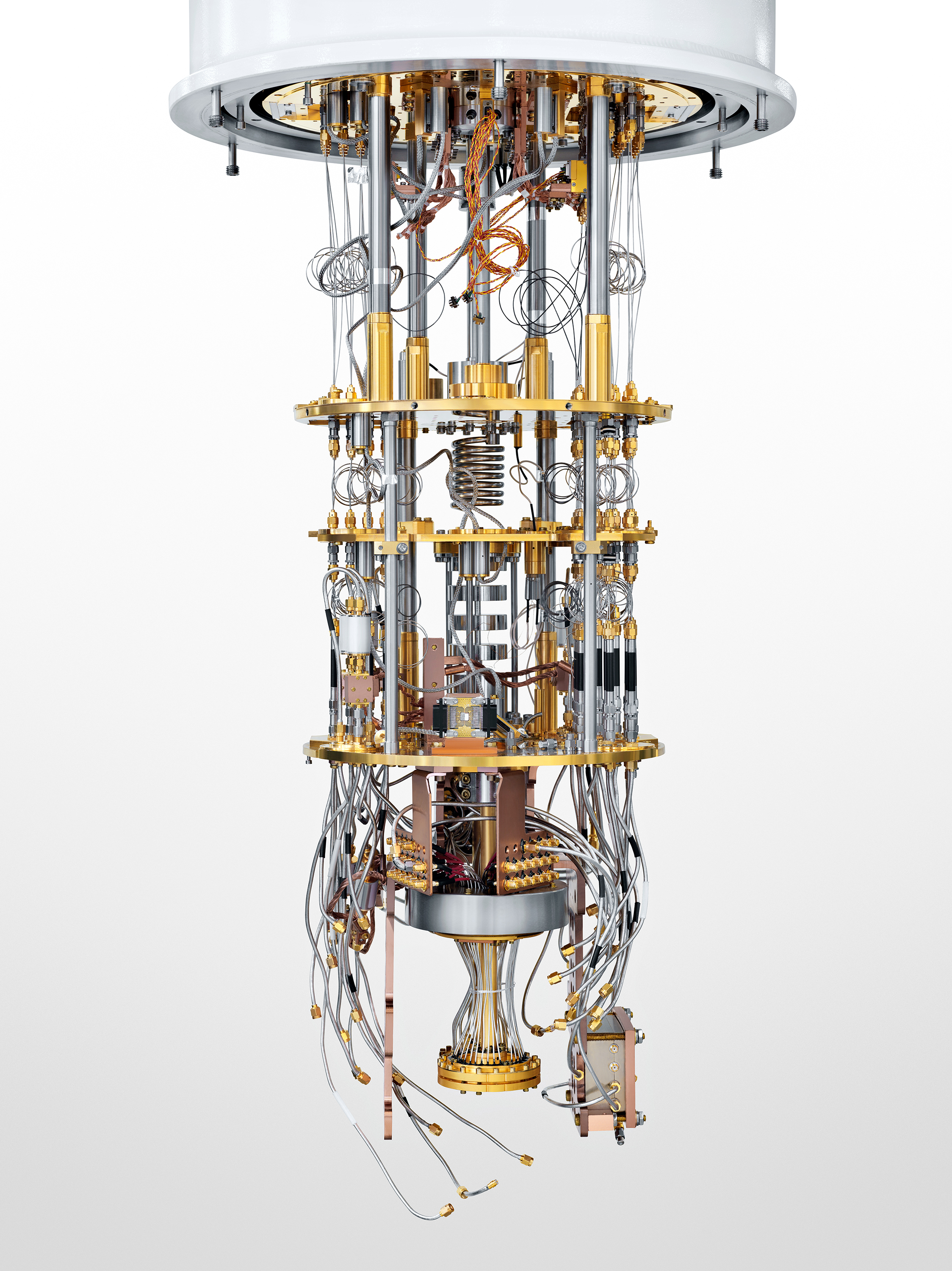
How does Quantum Computer works?
It starts with deciding how we will define a binary digit, or bit, when using a quantum object. For, say, an electron, we can describe each one as having a quality known as spin, a measure of how it rotates, at one of two extremes, “up” or “down,” and then assign the binary value 0 to an up spin and 1 to a down spin. (But it could equally be any other quantum object, like a photon or a molecule, with a different quality used to define the binary values.) This defines the quantum equivalent of a binary bit and is known as a qubit.
The electron follows quantum laws and can therefore exist with its spin undefined in a “superposition” state that is a complex combination of the 0 and 1 states. It will only become defined (as 0 or 1) if it interacts strongly with something in its environment, an interaction that quantum physicists often refer to as a measurement.
The process of defining the final outcome can change what you get. That process is called “interference.” When you assemble multiple qubits together, it’s possible to apply a certain set of starting conditions to each of those qubits — creating what quantum physicists call “interference effects” — that skew the undefined spins and set their interactions off on a particular course. Like waves rippling together on an ocean, they head toward an increased likelihood of the qubits arriving at a particular final state.
Superposition and interference alone are not quite enough to allow a quantum computer to beat a classical one. The vital third phenomena is known as “entanglement”. Entanglement arises between quantum particles that interact in particular ways, causing all their properties to become shared between the particles. The result is that measurements on one particle can affect the outcome of subsequent measurements on any particles entangled with it, even when they are not physically connected.
What is Big Data?
The term “Big Data” used for the large data collections done by large organizations. This data collection includes unstructured, semi-structured and structured data. Big data used in machine learning projects, predictive modelling and other advance applications.
From analyzing Big Data most of the industries can achieve better and faster decision-making, modelling and predicting of future outcomes and enhance business intelligence. As an example Healthcare big data analytics drive quicker responses to emerging diseases and improve direct patient care, the customer experience, and administrative, insurance and payment processing.
Big Data Analysis with Quantum Computing
Analyzing massive amounts of data or Big Data is very complex. In fact, it can be nearly impossible for humans to sift through a large volume of data and find correlated information that has actionable value. Organizations create so much data that large amounts of data go unused. Many are missing out on opportunities that could help gain competitive advantages.
Quantum computing is capable of administering large data sets at much faster speeds and can supply data to AI technologies to analyze data at a more granular level to identify patterns and anomalies. Quantum computing also can help integrate data by running comparisons between schemas to quickly analyze and understand the relationship between two counterparts. To give a bit of perspective, Google’s Sycamore is reported to have solved a problem in 200 seconds that would have taken today’s fastest supercomputer 10,000 years to solve. This opens new possibilities for the future of big data and analytics.
What might we expect in future?
Quantum computing can be a game-changer in massive industries and fields hence this super computers has a complex nature can be used to solve complex mathematical problems. The future of the quantum computing is lays in a superposition as its law. In near future we can experience a wide variety of applications from quantum computing. Such as in Big data analysis, machine learning, material science and Monte Carlo simulation. And there are large amount of quantum subject areas that can be massively developed to help he humans. Some of them are already commercially available for use. Some of the main subject areas are listed down below and known as to be developed in near future.
- Quantum cloud - Cloud-based quantum computing is a method for providing quantum computing by using emulators, simulators or processors through the cloud.
- Quantum cryptography – This concept aims to develop a secure encryption method by taking advantage quantum mechanical properties
- Quantum optics – This subject area of research to find a solutions to problems encountered in semiconductor technology and communication.
Even the quantum computing concept is being popular over the years but still there are several challenges. The quantum computers need extreme physical condition/environment to be operate and manufacturing quantum processors is quite challenging, But various large scale organizations such as Microsoft, IBM are trying to overcome those challenges. Let’s hope for a better future with Quantum computing.